Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Parkinson's Disease
Содержание
- 1. Parkinson's Disease
- 2. Parkinson DiseaseNeurological disease affecting over four million
- 3. Parkinson's disease was first formally described in
- 4. Appears Later in LifeContinuous Progressive Neurological Disease, thereby causing increasing disability of movement no cure
- 5. EtiologyCerebral atherosclerosisViral encephalitisSide effects of several antipsychotic drugs (i.e., phenothiazides, butyrophenones, reserpine)
- 6. Environmental factors and neurotoxinsPesticides, herbicides, industrial chemicals
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. In Terms of Etiology and Clinical Picture,
- 9. Usually Other Accompanied Autonomic Deficits Seen Later in Disease Process:Orthostatic HypotensionDementiaDystoniaOphthalmoplegiaAffective Disorders
- 10. Parkinson Disease NeurochemistryLoss of Dopaminergic (DA) Cells
- 11. Imbalance primarily between the excitatory neurotransmitter Acetylcholine and inhibitory neurotransmitter Dopamine in the Basal GangliaAChDA
- 12. The Dopaminergic Neurons in the Basal Ganglia
- 13. Basal GangliaThe Basal Ganglia Consists of Five
- 14. The balance of the five large Subcortical
- 15. Drug TherapyDrug Therapy Against ParkinsonDisease Is Aimed
- 16. Agents that Increase Dopamine functionsIncreasing the synthesis
- 17. Dopamine and Tyrosine Are Not Used for
- 18. L Dopa Therapy for Parkinson DiseaseDopamine Decarboxylase
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. L Dopa- PharmacokineticsL Dopa is readily absorbed
- 21. Effects of L Dopa on the Symptoms
- 22. Effects of L Dopa on BehaviorIn Terms
- 23. Effects of L Dopa on Cardiovascular SystemThe
- 24. Effects of L Dopa on Gastrointestinal SystemVery
- 25. GI cont.Some Patients Have Diarrhea and Some
- 26. Effects of L Dopa on Endocrine SystemL
- 27. Adverse Effects with L DopaMajor Problem with
- 28. Denervation SupersensitivityEffect Is Increased Postsynaptic TransmissionInitial Disappearance of Parkinson SyndromeOnset of Tardive Dyskinesia
- 29. Adverse Effects of L DopaSome are Irreversible
- 30. Adverse effects cont.See Cardiac Arrhythmia from Stimulation
- 31. Long Term TherapyBehavioral Disturbances in 20 to
- 32. TreatmentTreatment Is to reduce Dose and Put
- 33. "On/off" Effect"On/off" Effect Is like a Light
- 34. Treat by Giving Small Dose Regiments from
- 35. Drug Interactions with L DopaVitamin B6 -
- 36. Drug Interactions contCarbidopa Is Antagonistic to Peripheral
- 37. Drug Interactions contAntipsychotic Drugs - Antipsychotic Drugs
- 38. Drug Interactions contNonspecific MAO Inhibitors - Interfere
- 39. Other Drugs for Treating Parkinson DiseaseBefore Using
- 40. Bromocriptine for Treating Parkinson Disease ; an
- 41. Pramipexole is a nonergot dopamine agonist with
- 42. Amantadine for Treating Parkinson DiseaseAmantadine Effective as
- 43. Deprenyl ( Selegiline) for Treating Parkinson DiseaseDeprenyl
- 44. The Protective Effects of SelegilineAlthough the factors
- 45. Monoamine oxidase B Dopamine + 02 +
- 46. The evidence suggesting that oxidative reactions may
- 47. Amphetamine for Treating Parkinson DiseaseAmphetamine Has Been
- 48. Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors Tolcapone (Tasmar) and Entacapone (Comtan)
- 49. Antimuscarinic Agents for Treating Parkinson DiseaseThe Antimuscarinic
- 50. On the HorizonA number of potential Parkinson's
- 51. Слайд 51
- 52. Risk of Parkinsonism in smokers is 20-70%
- 53. Neural tissue transplants--Researchers are studying ways to
- 54. Скачать презентанцию
Parkinson DiseaseNeurological disease affecting over four million patients worldwide, over 1.5 million people in the U.S.. While it can affect individuals at any age, it is most common in the elderly.
- ВКонтакте
- РћРТвЂВВВВВВВВнокласснРСвЂВВВВВВВВРєРСвЂВВВВВВВВ
- РњРѕР№ Р В Р’В Р РЋРЎв„ўР В Р’В Р РЋРІР‚ВВВВВВВВРЎР‚
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Parkinson's Disease
Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D.
Howard University
College of Medicine
Department of Pharmacology
18
February 2002
Слайд 2Parkinson Disease
Neurological disease affecting over four million patients worldwide, over
1.5 million people in the U.S.. While it can affect
individuals at any age, it is most common in the elderly. The average age of onset is 55 years, although approximately 10 percent of cases affect those under age 40.Слайд 3Parkinson's disease was first formally described in "An Essay on
the Shaking Palsy," published in 1817 by a London physician
named James Parkinson, but it has probably existed for many thousands of years. Its symptoms and potential therapies were mentioned in the Ayurveda, the system of medicine practiced in India as early as 5000 BC, and in the first Chinese medical text, Nei Jing, which appeared 2500 years ago.Слайд 4Appears Later in Life
Continuous Progressive Neurological Disease, thereby causing increasing
disability of movement
no cure
Слайд 5Etiology
Cerebral atherosclerosis
Viral encephalitis
Side effects of several antipsychotic drugs (i.e., phenothiazides,
butyrophenones, reserpine)
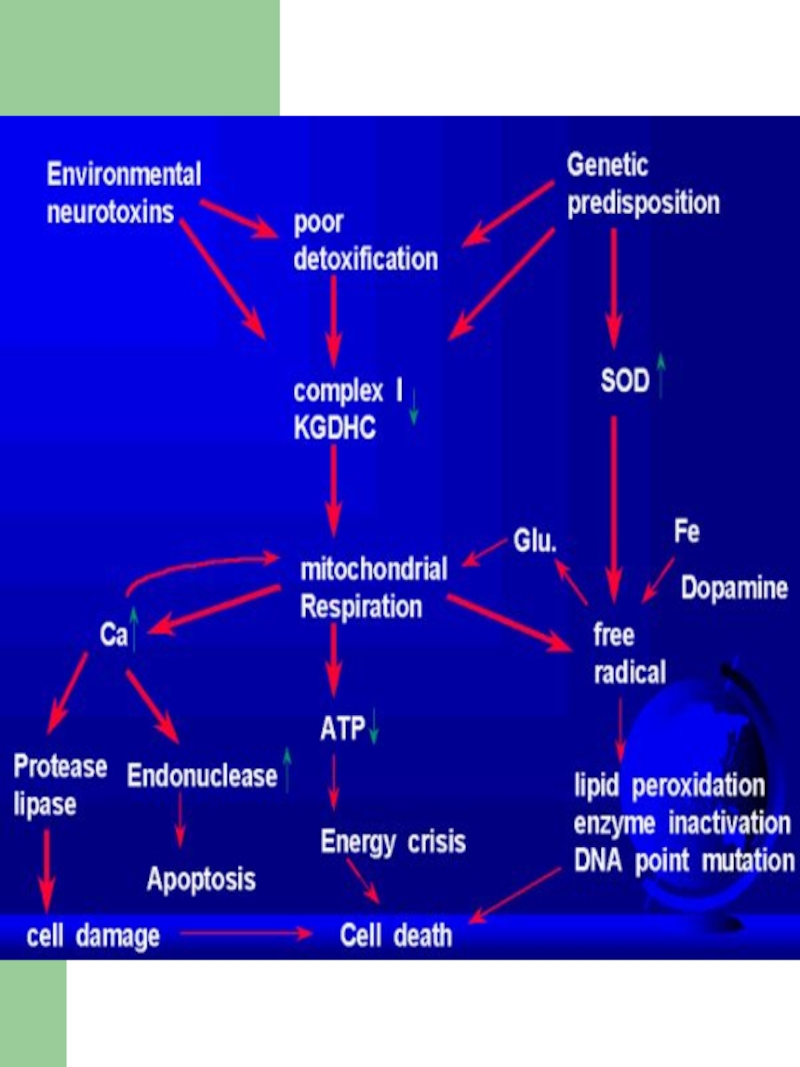
Слайд 6Environmental factors and neurotoxins
Pesticides, herbicides, industrial chemicals - contain substances
that inhibit complex I in the mitochondria
Слайд 8In Terms of Etiology and Clinical Picture, Major Symptoms Involve:
Bradykinesia-
Slowness in Initiation and Execution of Voluntary Movements
Rigidity - Increase
Muscle Tone and Increase Resistance to Movement (Arms and Legs Stiff)Tremor - Usually Tremor at Rest, When Person Sits, Arm Shakes, Tremor Stops When Person Attempts to Grab Something
Postural Instability - abnormal fixation of posture (stoop when standing), equilibrium, and righting reflex
Gait Disturbance - Shuffling Feet
Слайд 9Usually Other Accompanied Autonomic Deficits Seen Later in Disease Process:
Orthostatic
Hypotension
Dementia
Dystonia
Ophthalmoplegia
Affective Disorders
Слайд 10Parkinson Disease Neurochemistry
Loss of Dopaminergic (DA) Cells Located in Basal
Ganglia; most symptoms do not appear until striata DA levels
decline by at least 70-80%.Слайд 11Imbalance primarily between the excitatory neurotransmitter Acetylcholine and inhibitory neurotransmitter
Dopamine in the Basal Ganglia
ACh
DA
Слайд 12The Dopaminergic Neurons in the Basal Ganglia Are mainly affected
Acetylcholine
within striatum is a tonically activated neuron
It impinges on GABA
Neuron by an Excitatory ActionGABA Neuron Has an Inhibitory Action on the Substantia Nigra from Substantia Nigra, Has a Dopaminergic Feed Back Loop Back to Striatum Which Gets Loss Giving Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson Disease
Слайд 13Basal Ganglia
The Basal Ganglia Consists of Five Large Subcortical Nuclei
That Participate in Control of Movement:
Caudate Nucleus
Putamen
Globus Pallidus
Subthalamic Nucleus
Substantia Nigra
Слайд 14The balance of the five large Subcortical Nuclei are responsible
for smooth motor movements
The primary input is from the Cerebral
Cortex, and the output Is directed through the thalamus back to the Prefrontal, Premotor, and Motor CortexThe motor function of the basal ganglia are therefore mediated by the Frontal Cortex
Neurotransmitters in Basal Ganglia Include Serotonin, Acetylcholine, GABA, Enkephalin, Substance P, Glutamate, and Dopamine
Dopamine from Substantia Nigra decreases release of acetylcholine from striatum.
Слайд 15Drug Therapy
Drug Therapy Against Parkinson
Disease Is Aimed at Bringing the
Basal
Ganglia Back to Balance
Decrease Cholinergic Activity Within Basal Ganglia and
this Can Be Done Two Ways:Activating Dopamine receptors in Substantia Nigra feeding back to Cholinergic Cells in the striatum
Turn off the Cholinergic Cells, Then Things Are Brought Back to Balance
Antagonize Acetylcholine receptors
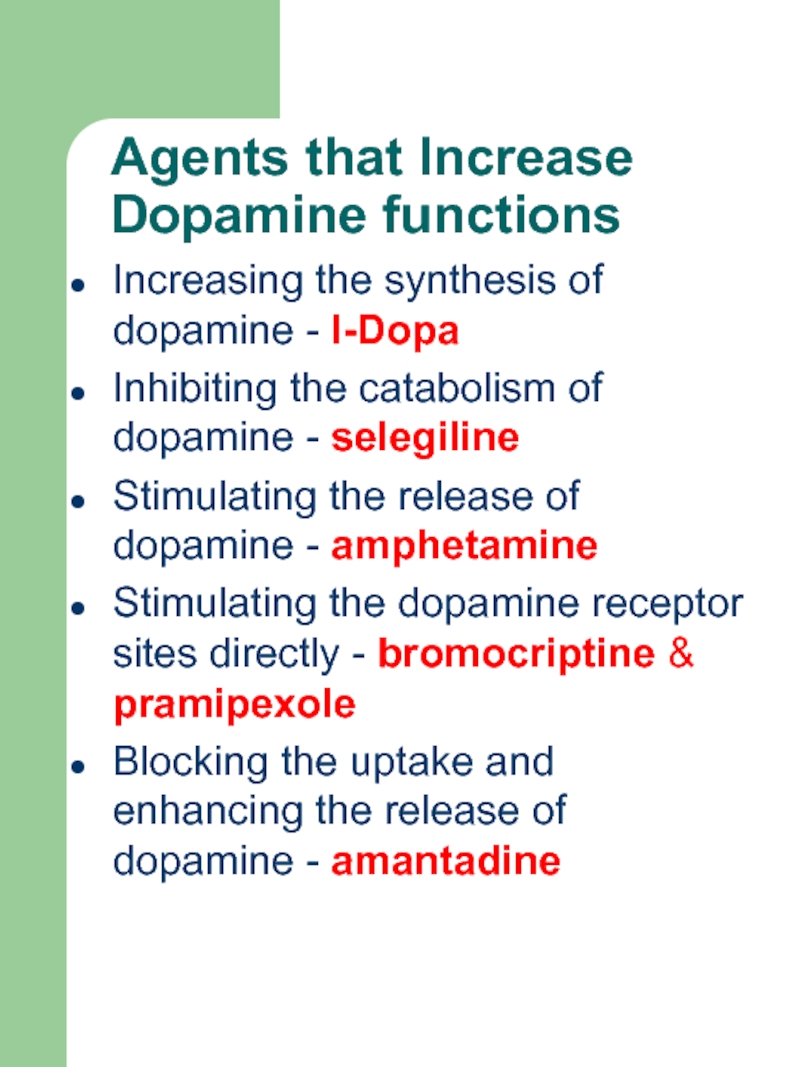
Слайд 16Agents that Increase Dopamine functions
Increasing the synthesis of dopamine -
l-Dopa
Inhibiting the catabolism of dopamine - selegiline
Stimulating the release of
dopamine - amphetamineStimulating the dopamine receptor sites directly - bromocriptine & pramipexole
Blocking the uptake and enhancing the release of dopamine - amantadine
Слайд 17Dopamine and Tyrosine Are Not Used for Parkinson Disease Therapy
Dopamine
Doesn't Cross the Blood Brain Barrier
Huge amount of tyrosine decreases
activity of rate limiting enzyme Tyrosine Hydroxylase That normally Converts Tyrosine to dopamine by overwhelming enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, has a feedback loop that will turn off tyrosine hydroxylaseСлайд 18L Dopa Therapy for Parkinson Disease
Dopamine Decarboxylase Converts L Dopa
to Dopamine That Gets Stored into Secretory Vesicles and Gets
Released from Basal GangliaСлайд 20L Dopa- Pharmacokinetics
L Dopa is readily absorbed from GI Tract
Usually
large doses must be given since ~1% actually cross Blood
Brain Barrier enters CNSLarge amount of L Dopa has to be given due to First Pass Effect
L Dopa metabolized by dopa decarboxylase in liver and periphery to dopamine
Secreted in urine unchanged or conjugated with glucoronyl sulfate
Most of L Dopa converted in periphery to NE and EPI
Слайд 21Effects of L Dopa on the Symptoms of Parkinson Disease
L
Dopa Fairly Effective in Eliminating Most of the Symptoms of
Parkinson DiseaseBradykinesia and Rigidity Quickly Respond to L Dopa
Reduction in Tremor Effect with Continued Therapy
L Dopa less Effective in Eliminating Postural Instability and Shuffling Gait Meaning Other Neurotransmitters Are Involved in Parkinson Disease
Слайд 22Effects of L Dopa on Behavior
In Terms of Behavior, L
Dopa Partially Changes Mood by Elevating Mood, and L Dopa
Increases Patient Sense of Well BeingSignificant Number of Patients Get Behavior Side Effects
Слайд 23Effects of L Dopa on Cardiovascular System
The Cardiovascular Effects Are
Cardiac Stimulation Due to Beta Adrenergic Effect on Heart
Treat with
Propranolol to Block Cardiac Stimulation EffectsMust be careful in treatment of elderly, most will have underlying cardiovascular problems, can transient tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias and hypertension
In Some Individuals, L Dopa produces Orthostatic Hypotension
Tolerance Will Develop Within Few Weeks
Слайд 24Effects of L Dopa on Gastrointestinal System
Very Common Gastrointestinal Effects
of L Dopa Include Nausea, Vomiting, and Anorexia
Probably Due to
Stimulation of Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone (CTZ) in MedullaTolerance Develops in a Few Weeks to this Effect
Other GI Disturbances Are Abdominal Pain
Слайд 25GI cont.
Some Patients Have Diarrhea and Some Patients Have Constipation
May
cause activation of Peptic Ulcer
Control Abdominal Effect by Giving Drug
in Low Doses and gradually increase dose.Give Drug with some food so as to have something in Stomach
Слайд 26Effects of L Dopa on Endocrine System
L Dopa Conversion to
Dopamine
Causes decrease in Prolactin from Stimulation of Dopamine Receptors in
Tubularinfundibular SystemСлайд 27Adverse Effects with L Dopa
Major Problem with L Dopa Is
Denervation Supersensitivity of Receptors
Start out with Certain Number of Receptors
in Basal Ganglia and If Destruction of Dopaminergic Neurons, This will Increase Dopamine Receptors postsynapticallyL Dopa Therapy Will Then Increase Dopamine at Synaptic Cleft, but Would Now Have Too Many Receptors Leading to Denervation Supersensitivity
Слайд 28Denervation Supersensitivity
Effect Is Increased Postsynaptic Transmission
Initial Disappearance of Parkinson Syndrome
Onset
of Tardive Dyskinesia
Слайд 29Adverse Effects of L Dopa
Some are Irreversible and Dose Dependent
However,
Long Term Therapy with L Dopa Not Associated with Renal
or Liver EffectsEarly in Therapy, 80% of Patients Have Nausea and Vomiting Due to Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone Stimulation
30% of Patients have Orthostatic Hypotension; So must Carefully Regulate Dose
Слайд 30Adverse effects cont.
See Cardiac Arrhythmia from Stimulation of Adrenergic Receptors
in Heart (Autonomic lecture). Adjust Dose for People with Cardiac
Problems50% of Patients Have Abnormal Involuntary Movements; ie. grimacing of face and tongue movements; slow writhing type of movements (Not Jerky Movements) in Arm and Face
This Is Due to High Dose of Dopa and Occurs Early in Therapy at 2 to 4 Weeks
Best Way to Handle Is by Reducing Dose
Слайд 31Long Term Therapy
Behavioral Disturbances in 20 to 25% of Population
Trouble
in Thinking (Cognitive Effects)
L Dopa Can Induce:
Psychosis
Confusion
Hallucination
Anxiety
Delusion
Some Individuals develop Hypomania
Which Is Inappropriate Sexual Behavior; "Dirty Old Man", "Flashers"Слайд 32Treatment
Treatment Is to reduce Dose and Put Person on Drug
Holiday Where Stop All Medication for 3-21 Days and Then
Slowly Reinitiate Therapy to Gradually increasing doses.Слайд 33"On/off" Effect
"On/off" Effect Is like a Light Switch ; Without
Warning, All of a Sudden, Person Goes from Full Control
to Complete Reversion Back to Bradykinesia, Tremor, Etc. Lasting from 30 Minutes to Several Hours and Then Get Control Again"On/off" Effect Occurs after usually after 2 or more years on L Dopa
Related to Denervation Hypersensitivity
Слайд 34Treat by Giving Small Dose Regiments from 16 to 20
Hours
"On/off" Effect May Be Due to Composite of Amino Acids
That Use Same Dopamine Transportor across Gastric Mucosa causing extremely low levels of L Dopa in CNS thereby causing symptoms of Parkinson Disease to reappear.Changing diet (to low protein), may cause large conc of L Dopa in CNS Giving thus producing an 'off' Effect of Symptoms of Parkinson Disease
Слайд 35Drug Interactions with L Dopa
Vitamin B6 - Vitamin B6 Is
a Cofactor for Decarboxylation of L Dopa; Vitamin B6 Enhances
Conversion of L Dopa to Dopamine in Periphery Making it less Readily for Use in the CNSL Dopa Is co-administered with Carbidopa
Слайд 36Drug Interactions cont
Carbidopa Is Antagonistic to Peripheral L Dopa Decarboxylation
Carbidopa Doesn't Cross Blood Brain Barrier
By co-administering Carbidopa, will decrease
metabolism of L Dopa in GI Tract and Peripheral Tissues thereby increasing L Dopa conc into CNS; meaning we can decrease L Dopa dose and also control the dose of L Dopa to a greater degree.Слайд 37Drug Interactions cont
Antipsychotic Drugs - Antipsychotic Drugs Block Dopamine Receptor
Reserpine
-Reserpine Depletes Dopamine Storage
Anticholinergics - Used Synergistically with L Dopa
as an Antiparkinson Agent, but Anticholinergics Act to decrease L Dopa absorption since Anticholinergics have an effect on gastric emptying time which delays crossing of GI Membrane by L DopaСлайд 38Drug Interactions cont
Nonspecific MAO Inhibitors - Interfere with L Dopa
Breakdown and exaggerate the CNS effects the Nonspecific MAO Inhibitors
Can Precipitate Hypertensive Crisis by the tyramine-cheese effect (Tyramine Is Found in Cheese, Coffee, Beer, Pickles, Chocolate, and Herring), when given to a person taking a MAO Inhibitor Tyramine Is not broken down therefore producing a tremendous release of Norepinephrine)Слайд 39Other Drugs for Treating Parkinson Disease
Before Using Other Drugs, First
Use L Dopa until Dosage of L Dopa Starts Becoming
too high for the Patient; L Dopa's Therapeutic and Toxicity Index Figures become too closeСлайд 40Bromocriptine for Treating Parkinson Disease ; an Ergotamine derivative, acts
as a Dopamine Receptor Agonist the Drug Produces Little Response
in Patients That Do Not React to LevodopaСлайд 41Pramipexole is a nonergot dopamine agonist with high relative in
vitro specificity and full intrinsic activity at the D2 subfamily
of dopamine receptors, binding with higher affinity to D3 than to D2 or D4 receptor subtypes.precise mechanism of action is unknown, although it is believed to be related to its ability to stimulate dopamine receptors in the striatum.
Слайд 42Amantadine for Treating Parkinson Disease
Amantadine Effective as in the Treatment
of Influenza, however has significant Antiparkinson Action; it appears to
Enhance Synthesis, Release, or Reuptake of Dopamine from the Surviving Nigral NeuronsСлайд 43Deprenyl ( Selegiline) for Treating Parkinson Disease
Deprenyl Selectively Inhibits Monoamine
Oxidase B Which Metabolizes Dopamine, but Does Not Inhibit Monoamine
Oxidase a Which Metabolizes Norepinephrine and SerotoninСлайд 44The Protective Effects of Selegiline
Although the factors responsible for the
loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease are not
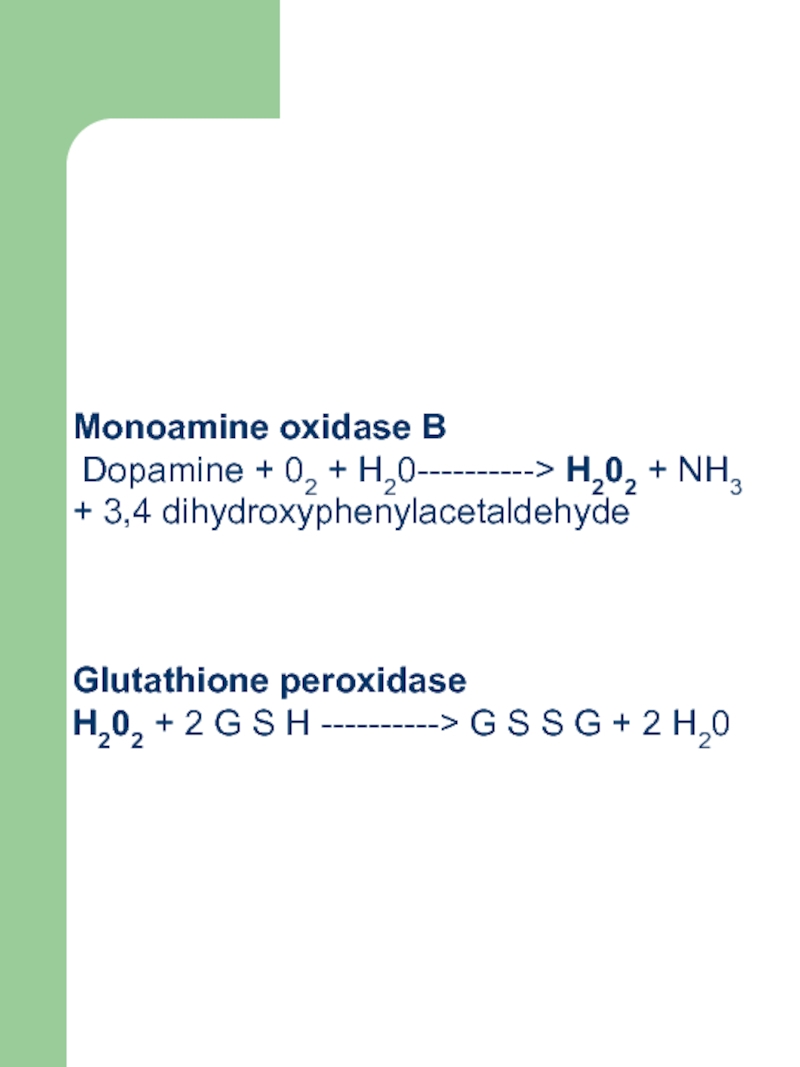
understood, the findings from neurochemical studies have suggested that the surviving striatal dopamine neurons accelerate the synthesis of dopamine, thus enhancing the formation of H202 according to the following scheme.Слайд 45Monoamine oxidase B
Dopamine + 02 + H20----------> H202 +
NH3 + 3,4 dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde
Glutathione peroxidase
H202 + 2 G S H
----------> G S S G + 2 H20Слайд 46The evidence suggesting that oxidative reactions may contribute to the
patho-genesis of Parkinson's disease includes the following.
In patients with
Parkinson's disease, the iron content is increased in the substantia nigra, the ferritin level is decreased in the brain, and the glutathione concentration is decreased in the substantia nigra. Furthermore, although 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is not itself toxic, when oxidized by monoamine oxidase B to the methylphenylpyridium ion, it becomes a selective nigral toxin that interferes with mitochondrial respiratory mechanisms. The toxicity of MPTP may be prevented by pretreatment with a monoamine oxidase B inhibitor such as selegiline.
Слайд 47Amphetamine for Treating Parkinson Disease
Amphetamine Has Been Used Adjunctively in
the Treatment of Some Parkinsonian Patients it Is Thought That,
by Releasing Dopamine and Norepinephrine from Storage Granules, Amphetamine Makes Patients More Mobile and More MotivatedСлайд 48Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors
Tolcapone (Tasmar) and Entacapone (Comtan) are two well-studied
COMT inhibitors.
Increases the duration of effect of levodopa dose
Can increase
peak levels of levodopaShould be taken with carbidopa/levodopa (not effective used alone)
Can be most beneficial in treating "wearing off" responses
Can reduce carbidopa/levodopa dose by 20-30%
Слайд 49Antimuscarinic Agents for Treating Parkinson Disease
The Antimuscarinic Agents Are Much
less Efficacious than Levodopa, and These Drugs Play Only an
Adjuvant Role in Antiparkinson Therapy the Actions of Atropine, Scopolamine, Benztropine, Trihexyphenidyl, and Biperiden Are SimilarСлайд 50On the Horizon
A number of potential Parkinson's treatments in research
laboratories now show much promise. They include:
Neurotrophic proteins--These appear
to protect nerve cells from the premature death that prompts Parkinson's. One hurdle is getting the proteins past the blood-brain barrier. Neuroprotective agents--Researchers are examining naturally occurring enzymes that appear to deactivate "free radicals," chemicals some scientists think may be linked to the damage done to nerve cells in Parkinson's and other neurological disorders.
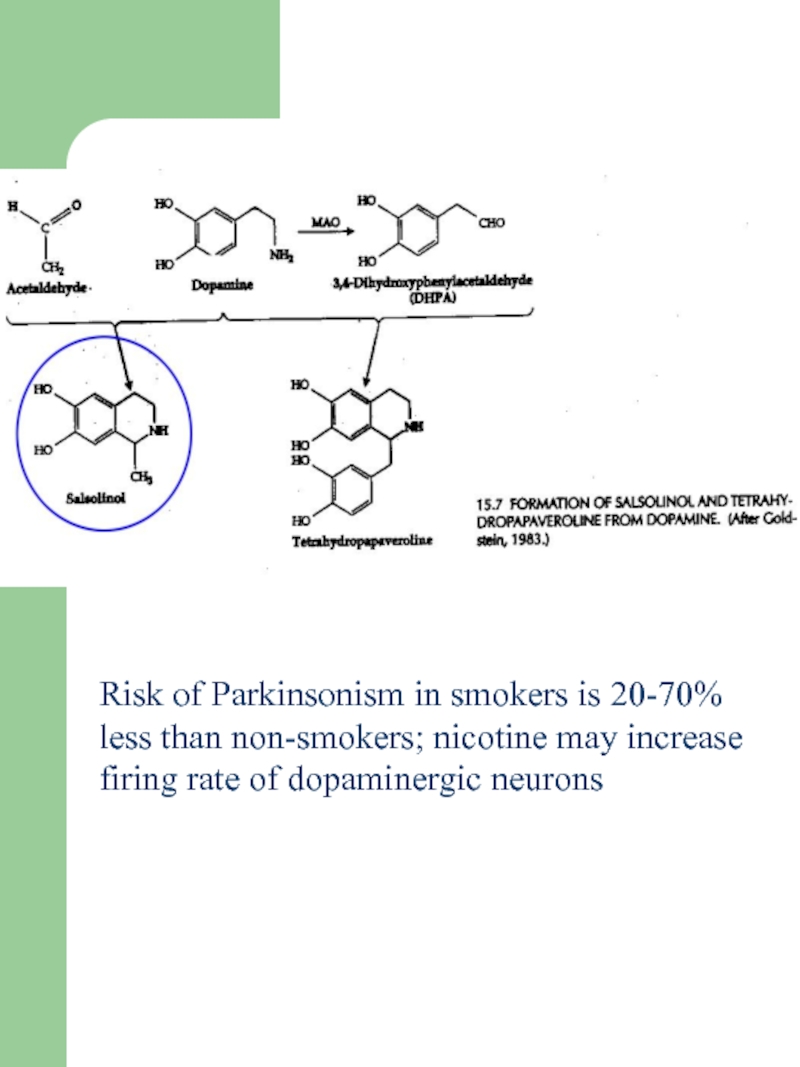
Слайд 52Risk of Parkinsonism in smokers is 20-70% less than non-smokers;
nicotine may increase firing rate of dopaminergic neurons
Слайд 53Neural tissue transplants--Researchers are studying ways to implant neural tissues
from fetal pigs into the brain to restore the degenerate
area. In a clinical trial conducted in part at Boston University School of Medicine, three patients out of 12 implanted with the pig tissues showed significant reduction in symptoms.Genetic engineering--Scientists are modifying the genetic code of individual cells to create dopamine-producing cells from other cells, such as those from the skin.
?????????